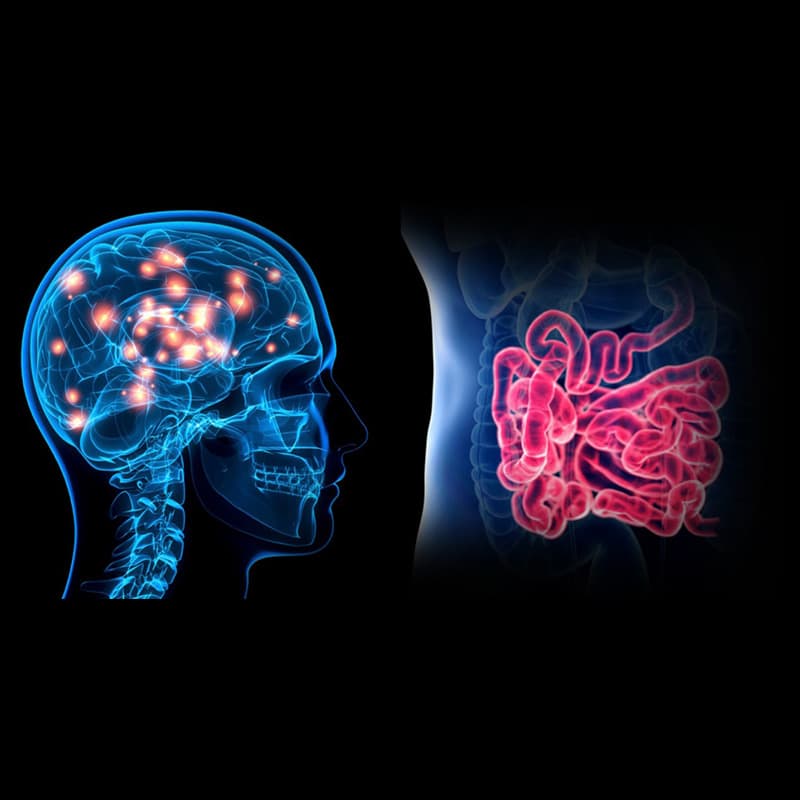
The vagus nerve is a key part of the gut-brain axis, linking the digestive system to the brain. It’s the longest cranial nerve, stretching from the brainstem to the abdomen. This nerve facilitates communication between the gut and the brain, enabling information exchange. It regulates various bodily functions like digestion, heart rate, respiration, stress response, and emotions.
What is the Vagus Nerve?
The Vagus Nerve, known as the “wandering nerve,” is a cranial nerve that extends from the brain stem to the abdomen. It plays a crucial role in regulating involuntary functions of the body. As the longest of the 12 cranial nerves, it forms an intricate network of connections. The Vagus Nerve is a vital component of the gut-brain axis, facilitating communication between the digestive system and the brain. This connection enables the exchange of information, influencing digestion, mood, and even immunity. Understanding the significance of the Vagus Nerve and its role in the gut-brain axis empowers us to maintain a harmonious balance within our bodies.
The Role of the Vagus Nerve in the Gut-Brain Axis
The vagus nerve plays a crucial part in the gut-brain axis, serving as a biological superhighway for communication between the brain and the gut. It has significant implications for our understanding of health from a biological perspective.
- Regulation of the Enteric Nervous System (ENS): The vagus nerve oversees much of the ENS, the independent “second brain” in our gut. It sends sensory information to the brain regarding gut health, inflammation, and biome balance.
- Influence on Mood and Mental Well-being: Through its role in the gut-brain axis, the vagus nerve has a direct influence on our mood and mental well-being. Imbalances in the gut microbiome may stimulate the vagus nerve to send signals to the brain, impacting mood, stress levels, and overall mental health.
- Connection to Physical Health: Not only limited to mental health, but the vagus nerve also plays a role in various physical functions like heart rate, digestion, and immune response, further underlining its essential role in a biological health approach.
Understanding the role of the vagus nerve allows for a more holistic approach to health, integrating the complex relationship between our brain, gut, and overall well-being.
The Benefits of Stimulating the Vagus Nerve
Stimulating the vagus nerve presents a host of benefits that can significantly improve overall wellbeing. The vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve in the body, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis by influencing the functioning of various organs.
- Physical Health: Regular vagus nerve stimulation can help lower heart rate and blood pressure, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, it also aids digestion and reduces inflammation throughout the body.
- Mental Health: This stimulation is also linked with improved mental health outcomes. It can diminish symptoms of depression and anxiety by helping to regulate mood and stress response.
- Emotional Wellbeing: By aiding the release of the ‘feel good’ hormone oxytocin, it contributes to greater emotional wellbeing, promoting feelings of tranquillity and relaxation.
Thus, stimulating the vagus nerve could serve as an integral part of a holistic approach to health and wellness.
How to Stimulate the Vagus Nerve
There are various techniques available to activate the vagus nerve, a crucial player in maintaining the body’s equilibrium and balance.
- Deep and Slow Breathing: Deep and slow breathing can stimulate the vagus nerve. This technique helps to reduce the heart rate and lower blood pressure, providing a sense of calmness.
- Cold Exposure: Brief exposure to cold can stimulate the vagus nerve. Cold showers, face splashing with icy water, or even drinking cold beverages can evoke this physiological response.
- Humming or Singing: The vagus nerve is connected to your vocal cords and the muscles at the back of your throat. Humming, chanting, or singing can activate these muscles and stimulate the vagus nerve.
- Meditation: Certain types of meditation, particularly those that involve focusing on the breath can stimulate the vagus nerve.
- Socializing and Laughing: The vagus nerve is also stimulated by socializing and laughing. Such activities can help to increase vagal tone. Vagal tone is the measure of how well your vagus nerve is functioning.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Both yoga and tai chi involve deep breathing and slow, intentional movements. These practices can activate the vagus nerve and promote relaxation.
- Massage or Acupuncture: Massaging certain pressure points or receiving acupuncture treatment can also stimulate the vagus nerve.
- Gargling: Gargling with water or mouthwash can activate the muscles in the back of your throat and stimulate the vagus nerve.
- Intermittent Fasting: Intermittent fasting has been found to increase vagal tone and promote overall health.
- Probiotics: Studies have shown that certain strains of probiotics can stimulate the vagus nerve and improve mood.
- Spending Time in Nature: Spending time in nature has been found to reduce stress and activate the vagus nerve. The sounds of birds chirping, the sight of greenery, and the fresh air can all have a positive effect on your vagal tone.
- Positive Thinking: Positive thinking can enhance your overall well-being and stimulate the vagus nerve. Focusing on gratitude, practicing affirmations, and finding joy in small moments can all contribute to this effect.
- Exercise: Regular exercise has been found to increase vagal tone and improve overall health. Activities such as running, cycling, swimming, and dancing can activate the parasympathetic nervous system and stimulate the vagus nerve.
Incorporating these techniques into your daily routine can help to stimulate the vagus nerve and promote overall well-being. It’s important to remember that everyone’s body is different, so some techniques may work better for you than others. Experiment with different methods and find what works best for you.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Gut-Brain Axis Connection
Maintaining a healthy gut-brain axis connection is critical for overall wellness, mood regulation, and even cognitive function. Here are some key tips to help you maintain and improve this vital connection:
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to your diet as it significantly impacts your gut health. Incorporate fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Avoid processed food and high sugar beverages.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity boosts your metabolism and encourages a healthy digestive system. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity every day.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress adversely affects your gut health, leading to issues like inflammation and gut imbalance. Incorporate stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness in your routine.
- Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep plays a vital role in maintaining the gut-brain axis. Aim for 7-9 hours of undisturbed sleep every night.
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: These beneficial bacteria and their food sources help improve gut health and, consequently, the gut-brain axis. Include foods like yogurt, kefir, and other fermented foods in your diet.
Remember, a healthy gut contributes to a healthy mind. Make these habits part of your lifestyle to enjoy a balanced gut-brain axis connection.
In conclusion, the vagus nerve is an important part of the gut-brain axis connection. It plays a vital role in regulating the body’s physiological functions and is essential for maintaining a healthy gut-brain axis connection. Stimulating the vagus nerve can have numerous benefits, including improved digestion, better mood, and reduced stress. To ensure a healthy gut-brain axis connection, it is important to practice regular stimulation of the vagus nerve, as well as to maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle. By understanding the importance of the vagus nerve and the gut-brain axis connection, we can take steps to ensure our overall health and wellbeing.